11 Types of Colonial Houses

Among the most popular residential architectural styles in the United States, Colonial homes can be seen in everything from new constructions to historic homes that date back decades or even centuries. This style of architecture is commonly found on the country’s east coast, where the majority of the population resided during the Colonial period.
There are 11 types of Colonial houses, such as Dutch, French, German, Georgian, and Neoclassical. British Colonial, Saltbox, and Spanish Colonial are among the most unique varieties. Colonial Revival and Cape Cod style are some of the most popular types of Colonial houses.
What is a Colonial House?
American Colonial style houses have a long history that spans hundreds of years and can be traced back as far as the 16th century. They were mostly constructed in the northeastern and southern parts of the United States. The style is reminiscent of homes found in England, Spain, and other areas across Europe as the Europeans were the ones who introduced their architectural influences to America.
Though, it wasn’t until the 1800s that architects and builders in the United States started to include distinctive designs, like extensive staircases, to these houses. Since that time period, Colonial structures have become a huge piece of American heritage and are highly sought-after by upper-class families for their sense of sophistication and poise. As such, they remain one of the most popular styles in the United States, even now.
Characteristics
Now that you understand what exactly a Colonial style home is, let’s take a look at the specific characteristics that set these houses apart from other architectural styles.
1. Exterior
In most cases, Colonial style houses are plain squares or symmetrical rectangles. Because of their minimalistic design, it’s often very easy to expand by adding onto the existing structure from the back or off of either side. These homes almost always feature wood siding on the front exterior, with paired windows on either side. Though, the exterior may also be stone, brick, or some other exterior material.
The front door is centralized, with an equal number of windows on each side. These houses usually have stone pillars supporting the curved roof above the front door. Colonial homes may also feature large porches or additional outdoor areas that serve as part of the house.
2. Interior
True Colonial homes typically have at least two stories, usually with bedrooms upstairs, a living area downstairs, and a staircase in the center of the hallway that acts as a focal point. The centralized position of the front door means that it opens up right in front of the staircase area. Grand entryways are a major design element that is common across most Colonial homes.
These homes seldom have an open floor plan. Instead, they’ll usually have a dining room positioned at the front of the house, and a living room and kitchen occupying the back half. Depending on the size, the house might also have a separate family room or great room. Most Colonial homes have about 3,000 square feet or more of total space.
Another distinguishing feature of Colonial homes is the central fireplace in the middle of the structure. Alternatively, there may be two fireplaces with one on each side of the house.
3. Neutral Colors
A large majority of Colonial style homes have a white exterior with black shutters. Though, it is also common to see almond, beige, cream, soft brown, or muted green hues used as exterior colors. Generally speaking, the colors will come from natural sources, like plants and minerals.
4. Double-hung Windows
Windows are a major design feature of Colonial homes. There should be an equal number positioned on either side of the front door. The windows themselves feature multiple moveable sashes that slide down from the top and are equal in terms of size.
5. Steep Roofs
A tell-tale sign that a house is Colonial style is when it features a pitched roof and no overhang. The roof will also have an oversized central or end chimney, along with various additional features such as pillars and brick detailing.
Types of Colonial Houses
Now that you are aware of the general characteristics of Colonial house, let’s examine the different types. Each type has corresponding unique features that set it apart from other colonial styles.
1. British Colonial
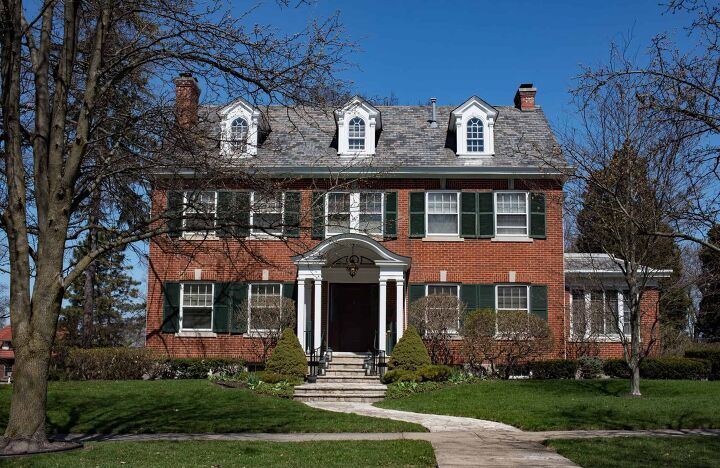
British Colonial homes are the most common style in the United States, mainly found in the northeastern part of the country. They were designed back in the 1600s by the original New England settlers, with their key feature being a wood-frame construction. British colonial houses are usually two stories with an open floor plan and a fireplace at the center. The exterior typically has lead-paned, diamond-shaped windows, while the roof features overlapping shingles. Key characteristics of this style include:
- Two stories
- Rectangular or symmetrical façade
- Casement windows
- Steep roofs – side gabled
Within the British style, there are a few subtypes with their own distinguishing characteristics:
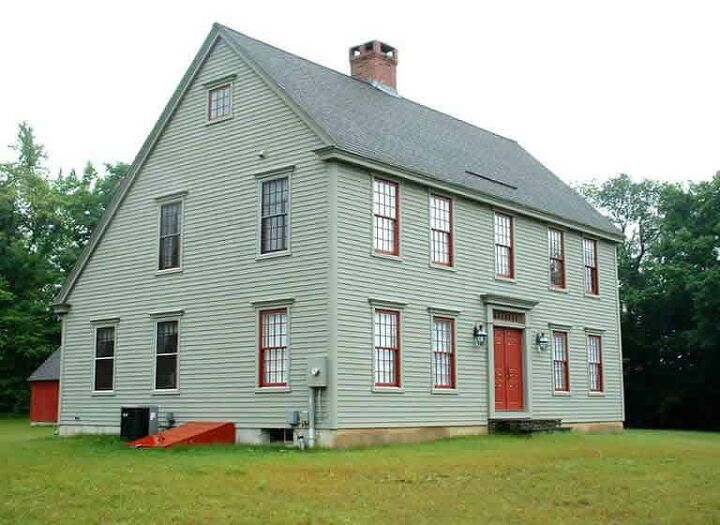
2. Saltbox Style
Saltbox style Colonials received their name from being constructed out of repurposed wood from salt containers. These houses were the standard in both the 17th and 18th centuries. The key features that set this style apart from the other British Colonial subtypes are an asymmetrical brick chimney, a roof that slopes on one side and extends all the way to the top, and a simple front.
3. Cape Cod Style
Beginning in Cape Cod, Massachusetts during the 17th century, Cape Cody Style Colonials were originally constructed by the Puritans who introduced their English origins to the United States with these half-timbered homes. The style consists of shingle or clapboard siding (usually weathered or a light gray hue), flat facades, a centrally positioned front door with two windows on each side, a central staircase, and a steep pitched side-gabled roof.
These types of British Colonials also have huge central chimneys and very little, if any, exterior ornamentation. Though most are two stories, some Cape Cod Style Colonials may only have one story with shutters to protect against inclement weather.
4. Georgian Style
Georgian style Colonials were a popular home type from 1700 to 1830. They were inspired by the four British monarchs that ruled during this time period, namely King George (I-IV). In most cases, these houses feature a brick exterior, though some may be stucco or stone. The colors of the exterior are traditionally red, white, or tan.
Distinguishing features of Georgian style Colonials are decorative entrances such as ogee caps, pediments, or arched tops, slightly-pitched roofs, decorative window headers, and paired chimneys. Central panel doors, with either Greek or Roman-inspired pillars, are another key feature of this style.
5. Mid-Atlantic Style
Mid-Atlantic style Colonials gained popularity thanks to Thomas Jefferson. These types of homes primarily existed throughout much of Virginia and New Jersey. When compared to other British colonials, this style is larger, more formal, and has more ornate decorative elements.
6. Dutch Colonial
The key distinguishing features of Dutch Colonial style homes are the roofs. These houses feature gambrel roofs, which were introduced to the United States by Dutch Colonists centuries ago. They were most popular from about 1625 to the mid-1800s, with the majority of them remaining in the state of New York.
Additional aspects of this style include brick or stone exteriors, flared eaves, and a single dormer with two or three windows. Though, some homes do not have any dormers at all. In most cases, the chimneys on these homes are positioned on the gable end. The roof design, with its two pitches, appears similar to a barn roof and are a signature for Dutch designs. Key characteristics of this style include:
- Constructed out of brick or stone
- Identical chimneys on either side of the house
- Symmetrical exterior
- Split doors that can be half-opened from the center
- Gambrel roof with wide shingles
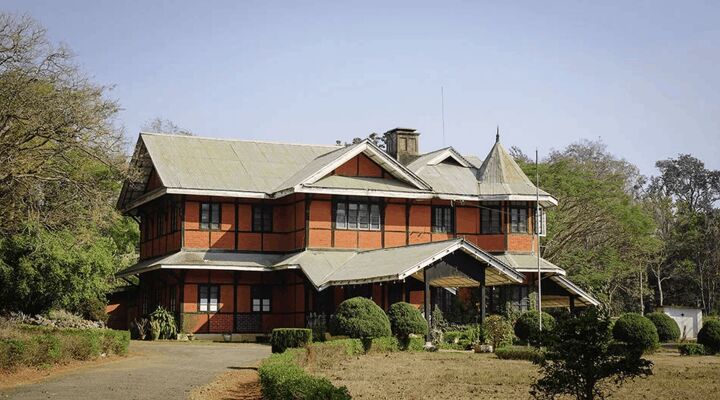
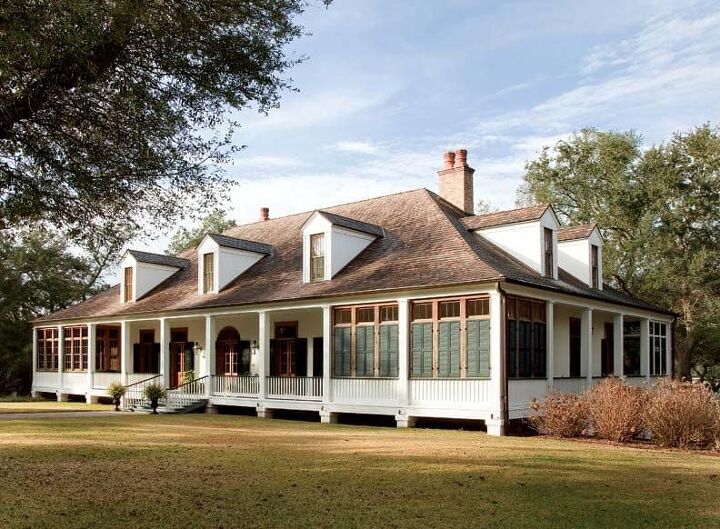
7. French Colonial
Unlike German, British and Dutch Colonial homes that are mostly found in the northern part of the country, French Colonial style houses primarily exist in the south. The French brought their design experience over from France during the 1700s, settling along the Mississippi Valley with the largest populations in Louisiana.
Similar to most other Colonial styles, French Colonials are constructed symmetrically with either a square or rectangular frame. They feature two stories, with the second floor used primarily as a living space. These homes also typically have raised piers with larger, open porches referred to as galleries that wrap around the house and are shielded by hipped roofs. Because of the high humidity and heat in the south, most rooms on the first floors open up to the extensive porch.
Many French Colonial homes will also have an open wrap-around porch on the second story. Another distinguishing feature of this style is ornate metalwork, usually displayed as wrought-iron columns or rails. Key characteristics of this style include:
- Porches are used for access to rooms rather than interior hallways
- French doors
- Intricate metalwork
- Wide porches that wrap around the house
- Made out of wood and brick, or a combination of mud and animal hair
- Roof extends over the porch
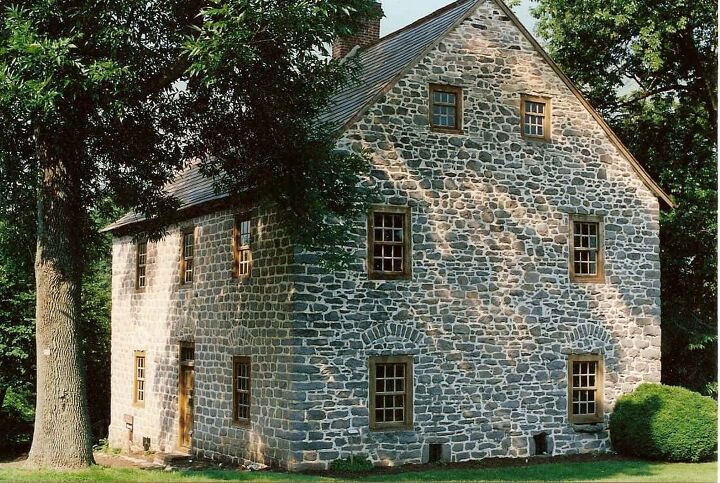
8. German Colonial
Somewhat similar to British Colonial homes, German Colonial style homes are also found primarily throughout the northeastern regions of the United States around the 1600s and mid-1800s. These homes are characterized by their thick exterior stone walls, often sandstone or limestone, huge beams, and exposed raw wood frames. They also have steeply-pitched roofs with side gables and centrally-positioned chimneys. Oftentimes, German Colonials will feature arches above the windows and doors on the first floor.
The main difference between British Colonials and German Colonials are the window casements. With German style Colonials, the window casements are symmetrical and positioned on the sides of the structure, with small arches atop each window. Key characteristics of this style include:
- Thick sandstone walls
- Wooden frame
- Symmetrical exterior design
- Reinforced arches above the door and windows on the first story.
9. Spanish Colonial
Originating in Mexico and Spain, Spanish Colonial style homes typically consist of exterior walls made out of stucco and are somewhat similar to American ranch style homes. These homes usually have one story with small windows that are usually secured with wrought iron metal, instead of traditional glass panes. The windows were designed this way during Colonial times because of the hot climate.
Other features of Spanish Colonials include clay tile roofs with a flat or minor pitch. These homes also have interior courtyards with rooms constructed around this central space, with usually some foliage, fountains, and a seating area. This is the only Colonial style that is traditionally one story. Key characteristics of this style include:
- Thick walls made form rocks or bricks and covered in stucco to help keep the home cool
- Interior shutters
- Single story
- Small windows and multiple exterior doors
- Clay tile or thatched roof
- Flat or slightly pitched roof
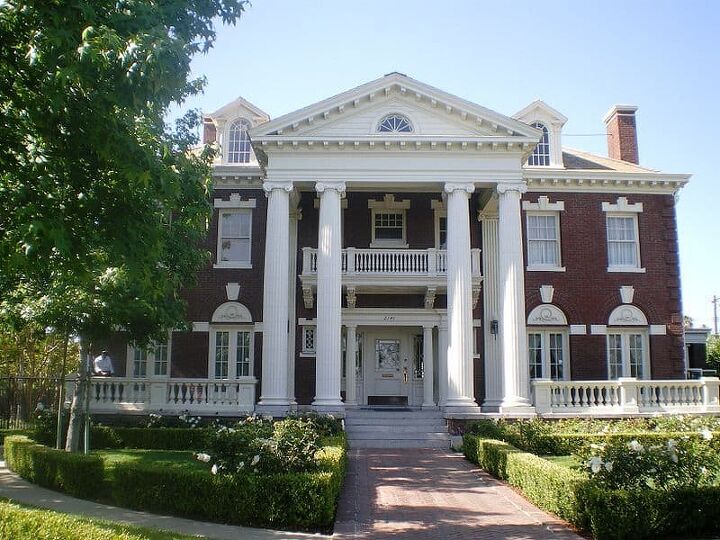
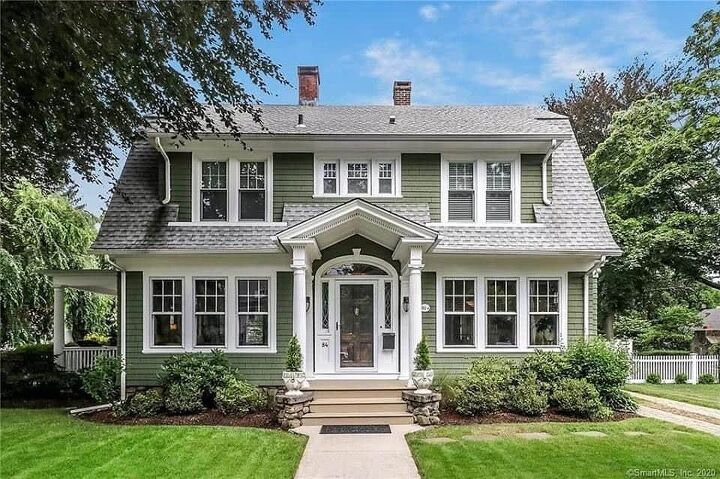
10. Colonial Revival
Dating back to the late 1800s, the Colonial Revival style combines various aspects of different Colonial style homes – primarily the Georgian style. The early settlers during the 1800s developed America’s heritage by building different styles of Colonial homes. The Revival period overlapped with the industrial revolution, which inspired handmade and decorative moldings around the ceilings of Colonial Revival homes. Bay windows on these houses are typically multi-paned, featuring proportional shutters. Key characteristics of this style include:
- Two to three stories
- Symmetrical exterior
- Decorative shutters
- Wood or brick exterior
- Intricate entrances, columns, and pillars
- Rectangular-shaped gable roof with a medium pitch
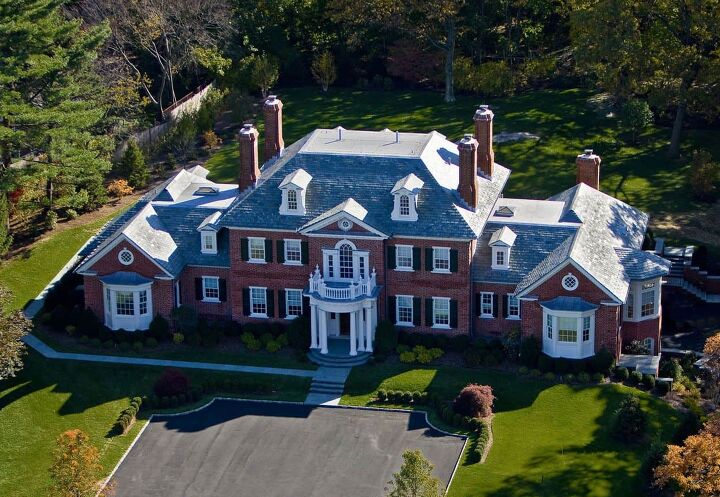
11. Neoclassical Colonial
Neoclassical Colonial style homes were introduced as a more modern alternative during the 21st century. They took inspiration from revival-style Colonial houses, though these homes used vinyl siding instead of more traditional materials.
Neoclassical Colonial homes usually have two stories, a square shape, side gable roofs, full-height porches, and decorative elements throughout the exterior. Architecturally speaking, they are traditional Colonial homes but they just use different materials. Key characteristics of this style include:
- Two or more stories
- Symmetrical exterior
- Ornate surrounds
- Hipped or side-gabled roofs
- Boxed eaves
- Double-hung window sashes
Related Questions
Do colonial houses have basements?
Colonial houses generally have basements. Both old and Colonial Revival houses often include basements, and they add value to the home. Unfinished basements are common in colonial houses, and you can increase resale value if you finish it.
Are colonial houses expensive?
Colonial houses are among the most expensive types of homes. They can be more expensive than Victorian houses in many areas. Luckily, it is cost-effective to build a colonial house rather than buy an existing one that is on the market.
Related Guides

Jessica considers herself a home improvement and design enthusiast. She grew up surrounded by constant home improvement projects and owes most of what she knows to helping her dad renovate her childhood home. Being a Los Angeles resident, Jessica spends a lot of her time looking for her next DIY project and sharing her love for home design.
More by Jessica Stone